INCONTINENCE
Urinary incontinence is the inability to control urination.
Urinary incontinence is the loss of bladder control, causing leakage of urine. In men, it can occur for several reasons, including prostate enlargement, prostatitis, or treatments for prostate cancer.
The term is sometimes used alongside Overactive Bladder (OAB), which involves frequent urination and a sudden, strong urge to go. Both conditions can interfere with daily life and are not a normal part of aging.
Many men feel embarrassed to talk about urinary leakage, but it is common and highly treatable. Millions of men in the United States experience incontinence, and the number increases with age, especially after prostate surgery or radiation. Because many men do not report symptoms, the true number affected is likely higher than current estimates.
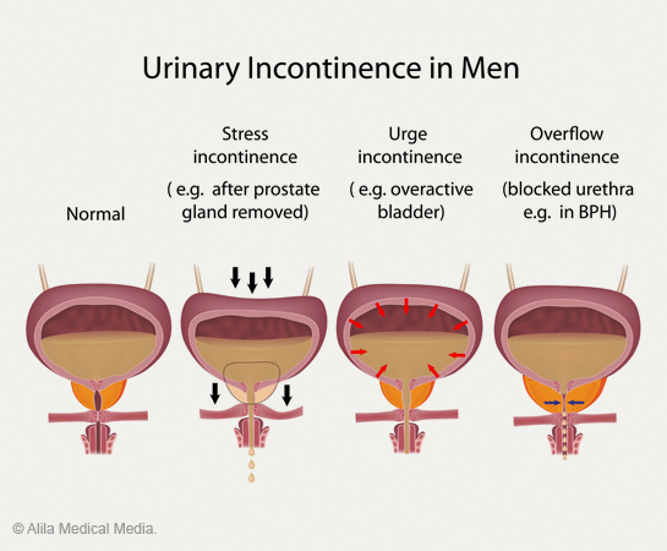
Types of Incontinence
Incontinence is classified by the symptoms of or circumstances occurring at the time of urine leakage.
-
Stress Incontinence
May be due to poor bladder support by the pelvic muscles or to a weak or damaged sphincter. This condition allows urine to leak when you do anything that strains or stresses the abdomen, such as coughing, sneezing, laughing, or even walking.
-
Urge Incontinence
Results when an overactive bladder contracts without your wanting it to do so. You may feel as if you can’t wait to reach a toilet. At times, you may leak urine without any warning at all. A bladder can become overactive because of infection that irritates the bladder lining. The nerves that normally control the bladder can also be responsible for an overactive bladder. In other cases, the cause may be unclear.
-
Mixed Incontinence
Is often a combination of both conditions above — stress and urge incontinence.
-
Overflow Incontinence
Occurs when the bladder is allowed to become so full that it simply overflows. This happens when bladder weakness or a blocked urethra prevents normal emptying. An enlarged prostate can result in such blockage. For this reason, overflow incontinence is more common in men that in women. Bladder weakness can develop in both men and women, but it happens most often in people with diabetes, heavy alcohol users, and others with decreased nerve function.
-
Environmental incontinence (sometimes called functional incontinence)
Occurs when people cannot get to the toilet or get a bedpan when they need it. The urinary system may work well, but physical or mental disabilities or other circumstances prevent normal toilet usage.
-
Nocturnal Enuresis
Incontinence that occurs during sleep
When individuals have two or more types of incontinence, the causes of each must be found and considered in planning appropriate treatment.
What to do about incontinence?
The first step is to locate a health care provider, such as a urologist, who is interested in and well-informed about treating incontinence. He or she will want to become familiar with your medical history and the way in which incontinence affects you. Be sure to come prepared for your visit with: (1) a list of all the medications you are currently taking, including those you purchase without a prescription; (2) the dates and outcomes of any bladder-related tests or surgical procedures you may have had; and (3) a bladder diary.
If you are seeking products to help with incontinence, click below to visit the Urology Health Store.
